
A Chinese proverb says, A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.
Curriculum development is the multi-level approach of creating and improvising the course material taught at a school, university, or educational institute. While the actual process varies from place to place, the broad framework incorporates analysis, building, implementation, and evaluation stages.
In the K-12 schools, the curricula are mostly developed at a local or state level to out-turn in standardized learning outcomes across different schools. Educators might get more individual flexibility to develop their curricula at the higher-education level. Either way, the individual or group is fully accountable for planning a course (and selecting strong k-12 course materials) to accomplish educational goals and meet student needs effectively. This blog will cover a complete overview of the curriculum development process.
We will cover the entire process systematically, like what will be taught, who will be taught, and how it will be taught. Each component affects and interacts with the other components. For example, how you teach a concept will affect the materials you use, which in turn affects student engagement. Keeping that in mind, it is important to plan out every step of the process carefully, ensuring that all lesson elements are cohesive and effective.
The term "curriculum" refers to the values-based actions and procedures that direct and support important learning experiences. A planned, thoughtful, and deliberate course of action, curriculum development ultimately improves the caliber and impact of the learning experience for students.
It entails the planning and coordination of educational activities that are intended to achieve specific learning objectives. It also necessitates evaluating those learning outcomes. The main intent of the curriculum is to raise the standard and significance of the teaching and learning process. Several factors must be considered to create meaningful learning experiences when designing a course or a program of study.
Curriculum development flows beyond a content-centered approach to one that takes into account the relationship between the learning outcomes of the course/program, how those outcomes are evaluated, and even the activities and opportunities intended to support student learning. When creating a course or program, curriculum developers must consider the following factors:
With an overview of the curriculum development process, teachers and students can outline what is essential for teaching and learning using the curriculum as a guide. The curriculum must include the necessary objectives, strategies, resources, and evaluations to ensure effective instruction.
Contact Us for Curriculum Development Services: https://www.acadecraft.com/contact-us/
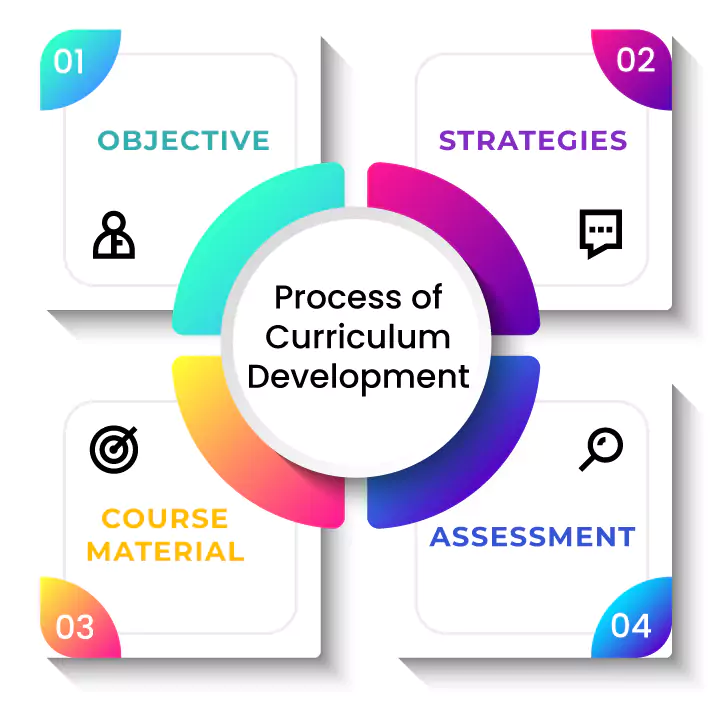 Objectives
ObjectivesThe expectations for instruction and learning within a curriculum are based on the course standards. Students are frequently given a clear understanding of the range of abilities and knowledge needed to accomplish an objective. The scope and extent of information that educators should teach must be included in the goals.
Strategies are instructional plans and practices that educators employ inside and outside the classrooms. These decisions support facilitating learning experiences to advance a student's capacity for comprehending and putting knowledge and abilities to use. Different approaches depend on the learner's needs, interests, task requirements, and learning environment. Strategies are changed based on the ongoing evaluation of students' progress toward achieving the goals.
Course Materials are the tools chosen to boost the productivity and achieve curriculum goals. These materials are purposefully chosen to aid a student's learning. The selection of course materials takes into account the interests of the students along with the global perspectives, cultural diversity, and different learner types.
Assessment is the ongoing method of collecting data concerning student learning in a curriculum. It covers a variety of ways to demonstrate what the student comprehends, knows, and is capable of doing in terms of knowledge and skills. Based on assessment data regarding instructional strategies, teaching resources, and academic support, decisions are made. This is to enhance the student's prospects and direct future instruction.
Curriculum planning focuses on implementing various organizational and instructional techniques to achieve the best possible student growth and learning outcomes. Teachers may base their curriculum on daily lesson plans, a particular assignment, a significant amount of coursework, specific sections of a class, or an entire educational program.
For instance, a teacher may implement a curriculum by breaking down a lesson into sections, assigning independent assignments or activities to each section, and then incorporating feedback on each activity into the next section.
They can also use various teaching techniques, such as lectures, practice sessions, individualized instruction, and group activities, to further the learning process. Moreover, teachers can deliver guidance and support to help students develop strategies for learning, such as time management and problem-solving skills.
Now that we've covered curriculum development and planning, let's move on to curriculum design. Curriculum design is the purposeful institution of course activities and execution within a classroom. When higher education instructors plan their curriculum, they consider the following:
Also Read: What is Curriculum Development? Why is it Important?
Three models of Curriculum Design and Development are learner-centered, problem-centered, and subject-centered. Let's understand each one of them in brief:
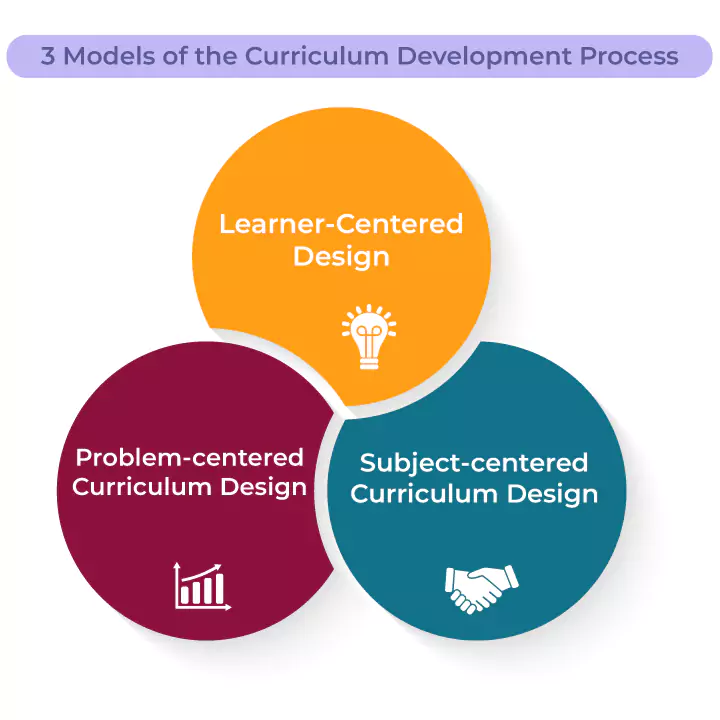
The learner-centered curriculum design emphasizes that every learner has unique and different characteristics. The teachers or educators are there to provide students with the opportunities to take ownership of a project or an assignment. They need to create possibilities for independent learning with well-regulated liberty.
It indicates that the students take a more active role in the classroom, which has to be done under the teacher's guidance. There are four distinctive attributes of learner-centered curriculum design, which includes:
Problem-centered curriculum design guides students to look at problems and formulate solutions. This model focuses on engaging students in authentic learning since they are exposed to real-world issues.
This type of curriculum designing has been shown to enhance the curriculum's relevance and boost creativity, teamwork, and innovation in classroom learning. The disadvantage of this model is that student needs are not always accounted for.
Subject-centered designing of curriculum revolves around a particular subject matter or field, such as literature, mathematics, or chemistry. This curriculum model design overlooks the subject rather than the student. This model is most popular under the standardized curriculum in K-12 public institutions.
Teachers compile a list of subjects and specific examples of how they should be explored and studied in classrooms. This procedure is common in large universities or college classrooms where professors or educators can focus on a specific subject or field.
Students are not the primary focus of subject-centered curriculum design, and the model focuses less on individual learning styles than other curriculum design methods. It can lead to student engagement and motivation issues and may cause students who are not responsive to this model to fall behind.
Teachers should consider all 3 models mentioned above in curriculum designing before planning and selecting the model best suited to their students and their course.
Curriculum development typically fits into a broad framework similar to several instructional design strategies. Each procedure looks like this:
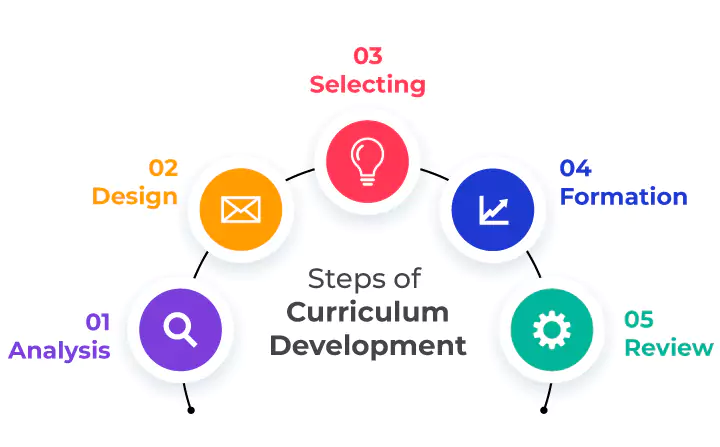
The framework you choose should consider these steps as a cycle rather than as a linear process for the most successful outcomes. This process ensures that you can revise the curriculum even once your course is in session.
In this blog, we have given you an overview of the curriculum development process. While developing a potent curriculum, educational institutions must follow its various steps and models.
When your course plans are finalized, you'll be eager to work with academic design professionals to develop specialized digital course materials that actively support your distinctive curriculum. It guarantees a student-focused approach throughout your entire course for better learning outcomes.
The curriculum development team assists faculty in developing and revising courses and programs to ensure the best possible student learning experience. We assist instructors in developing and updating their programs and curricula, which leads to meaningful change.
Interesting Read: 7 Strategies to Enhance Student Concentration
Share